Floods

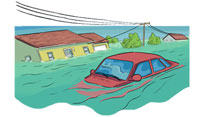
Floods have been recurrent phenomena in India from time immemorial. Almost every year floods of varying magnitude affect some parts of the country or the other. Different regions of the country have different climates and rainfall patterns and, therefore, while some parts face devastating floods, other parts may, at the same time, experience drought conditions.
The monsoon regime is a regular phenomenon. Year-to-year variations occur with regard to the onset of the monsoon, its progress over the Indian landmass, and the amount of rainfall distribution. The Indian subcontinent receives maximum rainfall during the south- west (SW) monsoon (summer monsoon) for a period of about 100 days, starting from the first week of June to the end September. Inadequate capacity of the rivers to contain within their banks the high flows brought down from the upper catchment areas following heavy rainfall, leads to flooding. Areas with poor drainage facilities get flooded by accumulation of water from heavy rainfall.